
Similar effects have been observed in epidemiological studies conducted in children.
#Solution precipitate calculator mac#
The proposed MAC of 0.1 mg/L (100 µg/L) is based on neurological effects observed in rodents. This expanded and updated document proposes both a maximum acceptable concentration (MAC) and an aesthetic objective for total manganese in drinking water. The existing guideline on manganese, last updated in 1987, established an aesthetic objective (AO) of 0.05 mg/L (50 µg/L), based on treatment limitations as well as taste and staining of laundry and plumbing fixtures. The purpose of this consultation is to solicit comments on the proposed guideline, on the approach used for its development and on the potential economic costs of implementing it, as well as to determine the availability of additional exposure data. The Federal-Provincial-Territorial Committee on Drinking Water (CDW) has assessed the available information on manganese with the intent of updating the current drinking water guideline and guideline technical document on manganese in drinking water.
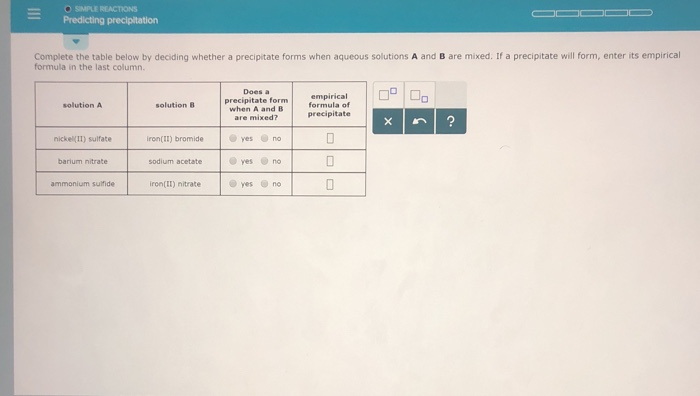
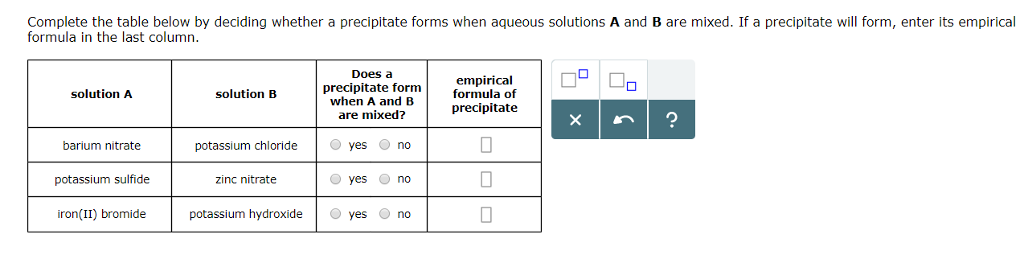
Chlorides are soluble in water with the exception of silver, lead and mercury. KNO 3 will remain in solution since all nitrates are soluble in water. The products should rearrange the ions to: What would be the expected products and will a precipitate form? The resulting balanced reaction would be:Ģ AgNO 3(aq) + MgBr 2 → 2 AgBr(s) + Mg(NO 3) 2(aq) The other compound Mg(NO 3) 2 will remain in solution because all nitrates, (NO 3) -, are soluble in water. Are the products soluble in water?Īccording to the solubility rules, all silver salts are insoluble in water with the exception of silver nitrate, silver acetate and silver sulfate.
The state of the products needs to be determined. The balanced reaction would be:Ģ AgNO 3(aq) + MgBr 2 → 2 AgBr(?) + Mg(NO 3) 2(?) For example, a silver nitrate solution (AgNO 3) is mixed with a solution of magnesium bromide (MgBr 2). The question remains, will AD or CB remain in solution or form a solid precipitate?Ī precipitate will form if the resulting compound is insoluble in water. This reaction is generally a double replacement reaction in the form: When two aqueous solutions are mixed, the ions interact to form products. These solutions are represented in chemical equations in the form: AB(aq) where A is the cation and B is the anion.
#Solution precipitate calculator how to#
This guide will show how to use the solubility rules for inorganic compounds to predict whether or not the product will remain in solution or form a precipitate.Īqueous solutions of ionic compounds are comprised of the ions making up the compound dissociated in water. When two aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are mixed together, the resulting reaction may produce a solid precipitate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
